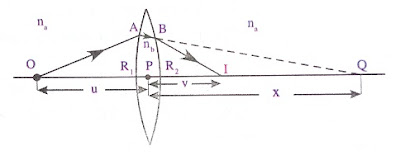
1. Place a thin lens (which is made of one convex
surface and one concave surface) between two refractive indices.
2. Let na be the refractive index of one
medium and and nb be the refractive index of second medium.
3. Consider an object O placed on the principal axis
of the thin lens.
4. Now consider a ray from object O incident on the
convex surface of the lens at point A
which has a radius of curvature R1.
5. If there is no concave surface, it forms an image
at Q then we take,
Object distance PO = -u, image distance PQ = v = x,
radius of curvature R = R1
6. For convex surface, n1 = na,
n2 = nb
7. According to image formation on curved surface
formula,
n2/v – n1/u = (n2 –
n1)/R
By substituting the values we get,
nb/x + na/u = (nb -
na)/R1 -----------------(1)
8. After getting refracted at point A again the ray
get refracted due to concave surface at point B and reaches on the principal
axis at point I.
Note:
The image Q of object O due to the convex surface is taken as the object for
the concave surface.
Here,
Object distance PQ = u = x, Image distance = PI = v,
radius of curvature = -R2
For concave surface n1 = nb, n2
= na
by substituting the values we get,
na/v – nb/x = (na -
nb)/(-R2) ---------------- (2)
Add eq (1) and (2) we get,
na/v + nb/u = (nb -
na)(1/R1 + 1/R2)
devide both sides by na,
1/v + 1/u = (nba - 1)(1/R1 +
1/R2)
here nba = nb/na,
is called the refractive index of lens with respect to the surrounding medium.
By using sign convention we get,
1/v – 1/u = (nba - 1)(1/R1 –
1/R2)
but we k now,
1/f = 1/v – 1/u
therefore we get,
1/f = (nba - 1)(1/R1 – 1/R2)
if the surrounding medium is air then nba
= n
1/f = (n - 1)(1/R1 – 1/R2) is
the equation of Lens Maker’s Formula.
Note:
1. The convex lens act as converging lens (if
refractive index of medium is less than refractive index of lens)
2. The convex lens acts as diverging lens (if
refractive index of medium is greater than refractive index of lens)